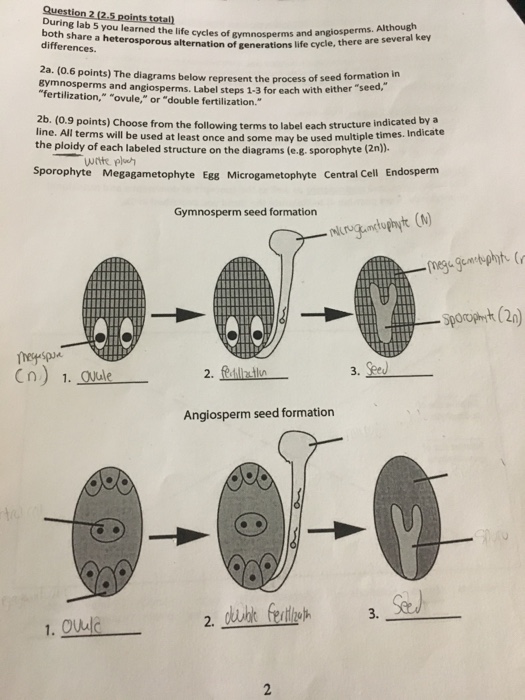
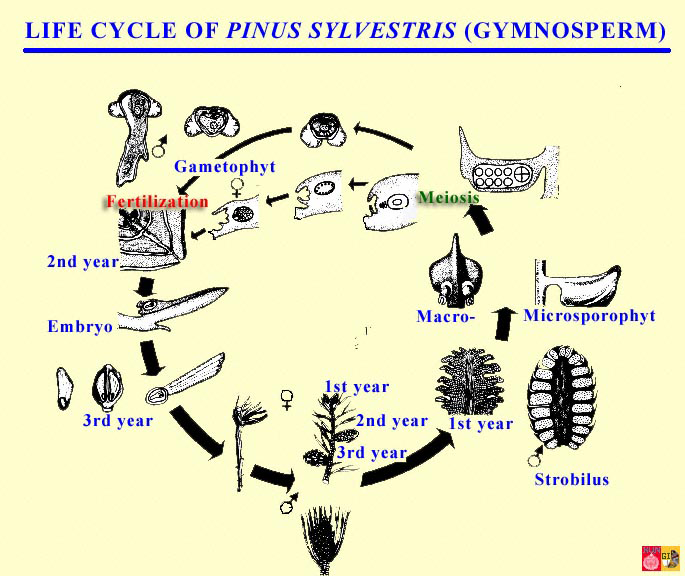
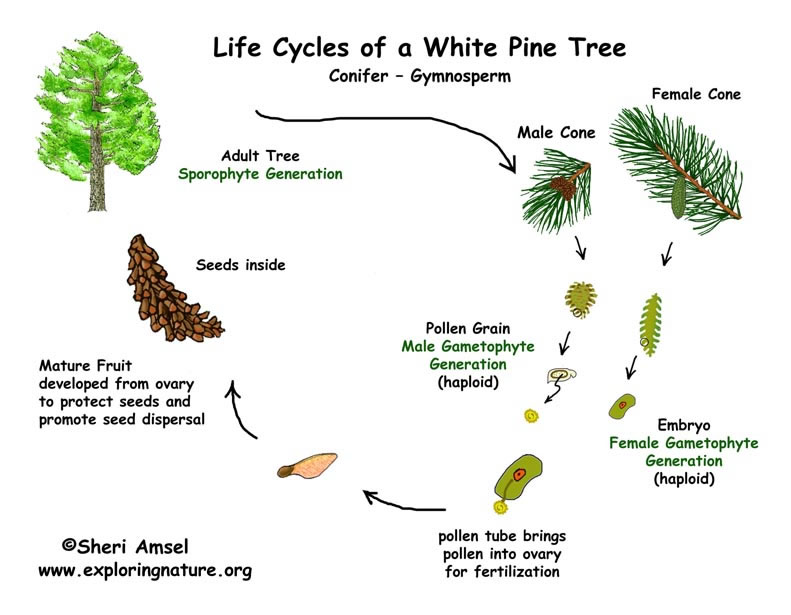
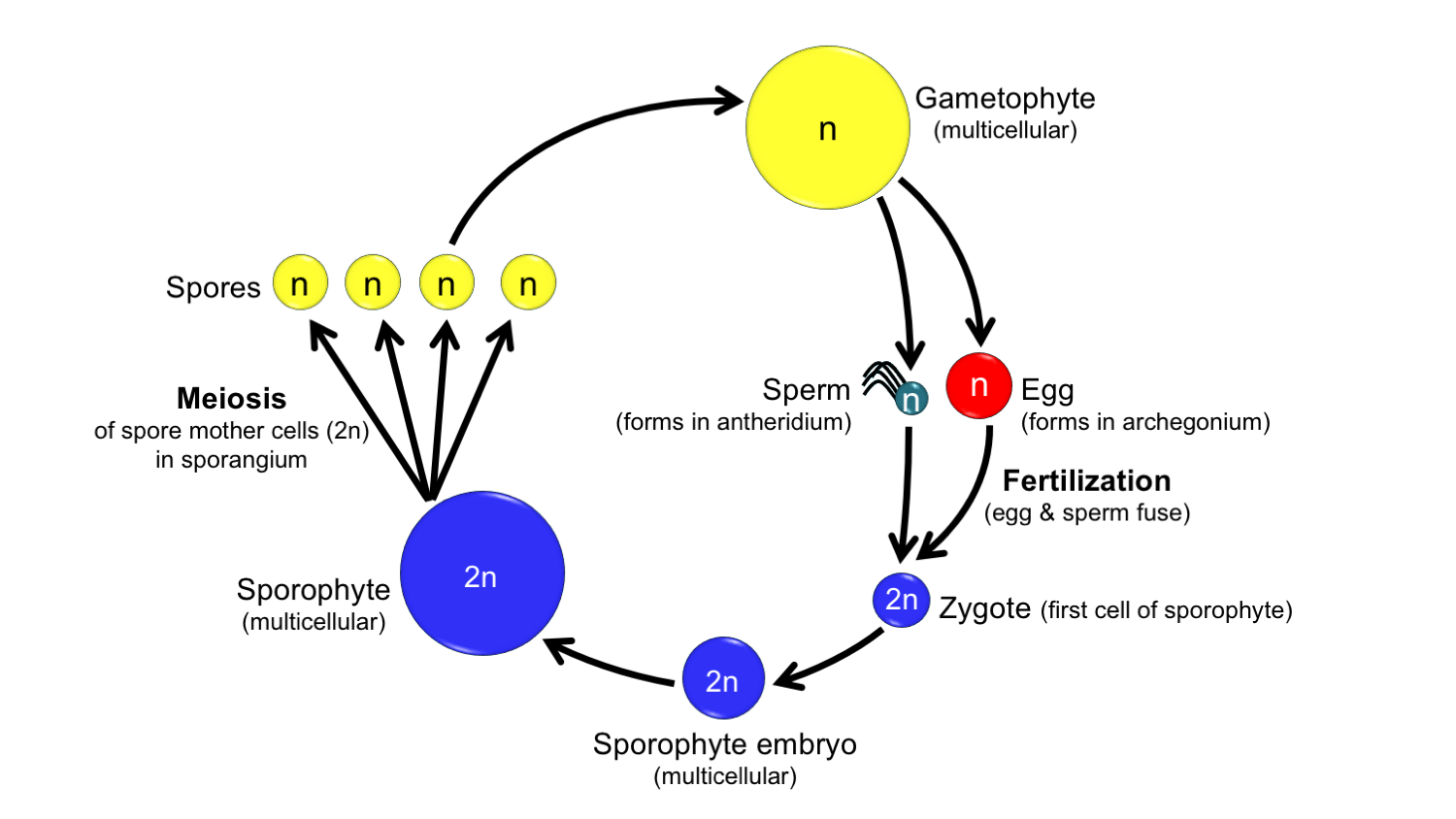
life cycle of gymnosperms and angiosperms
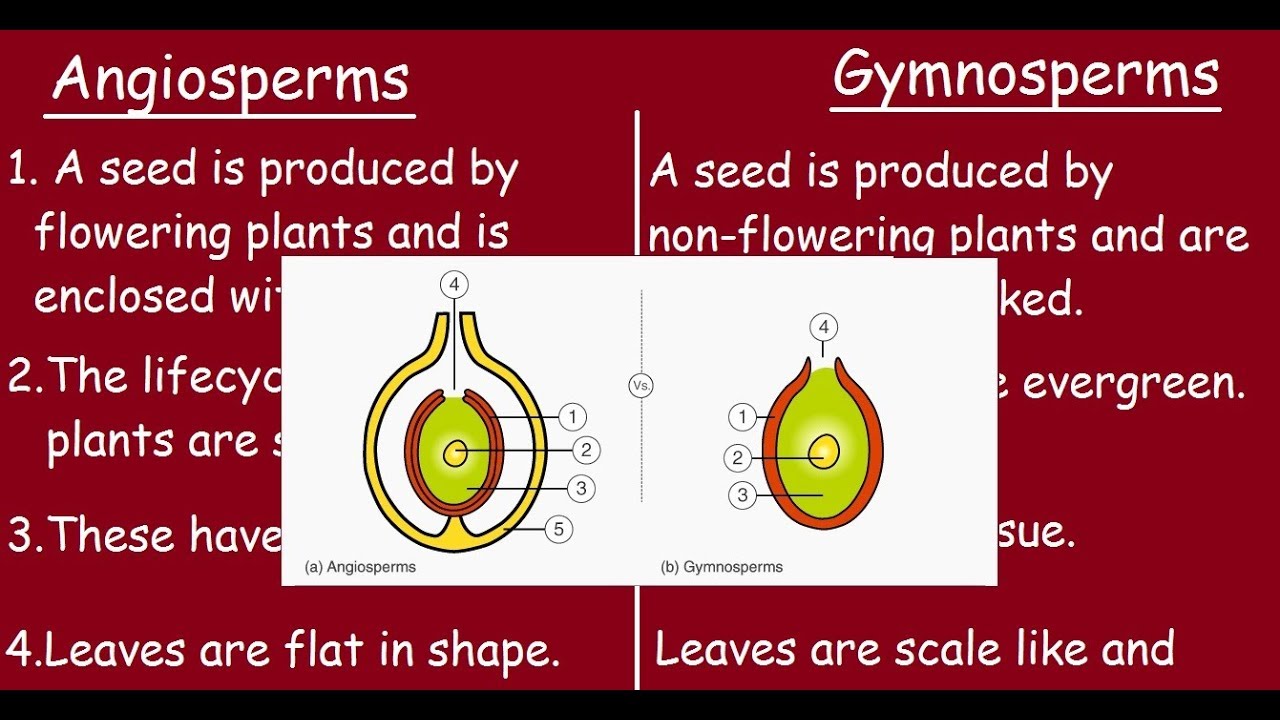
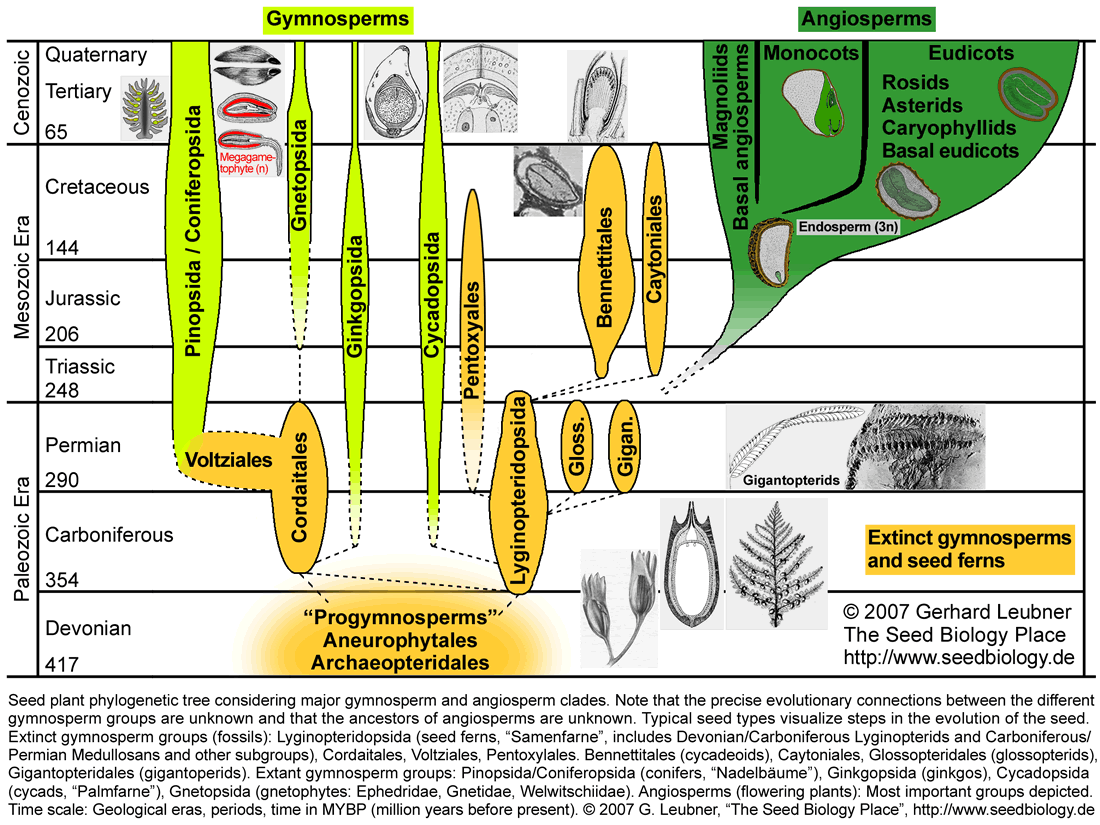
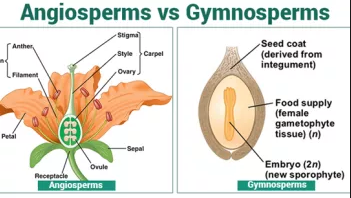
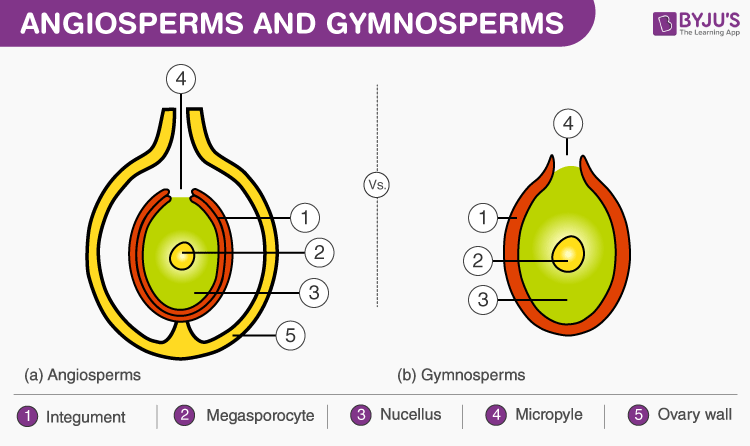
Angiosperms and gymnosperms are both seed bearing plants with a few similarities. Angiosperms and gymnosperms both utilize seeds as the primary means of reproduction and both use pollen to facilitate fertilization. This is due to the fact that gymnosperms were present for at least 200 million years before the angiosperms evolved and they may have shared a common ancestor.
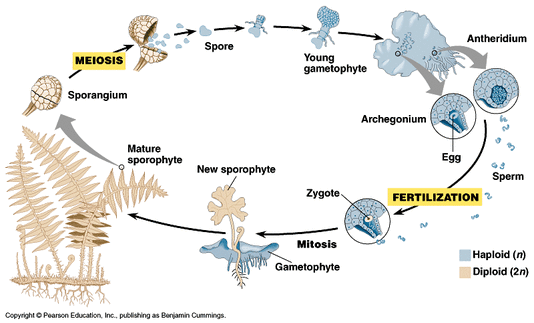
The sporophyte has special structures on the undersides of the fronds or leaves that produce spores.

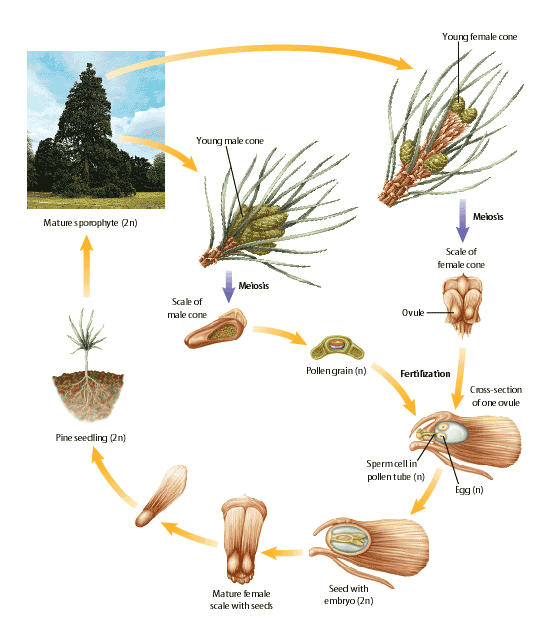
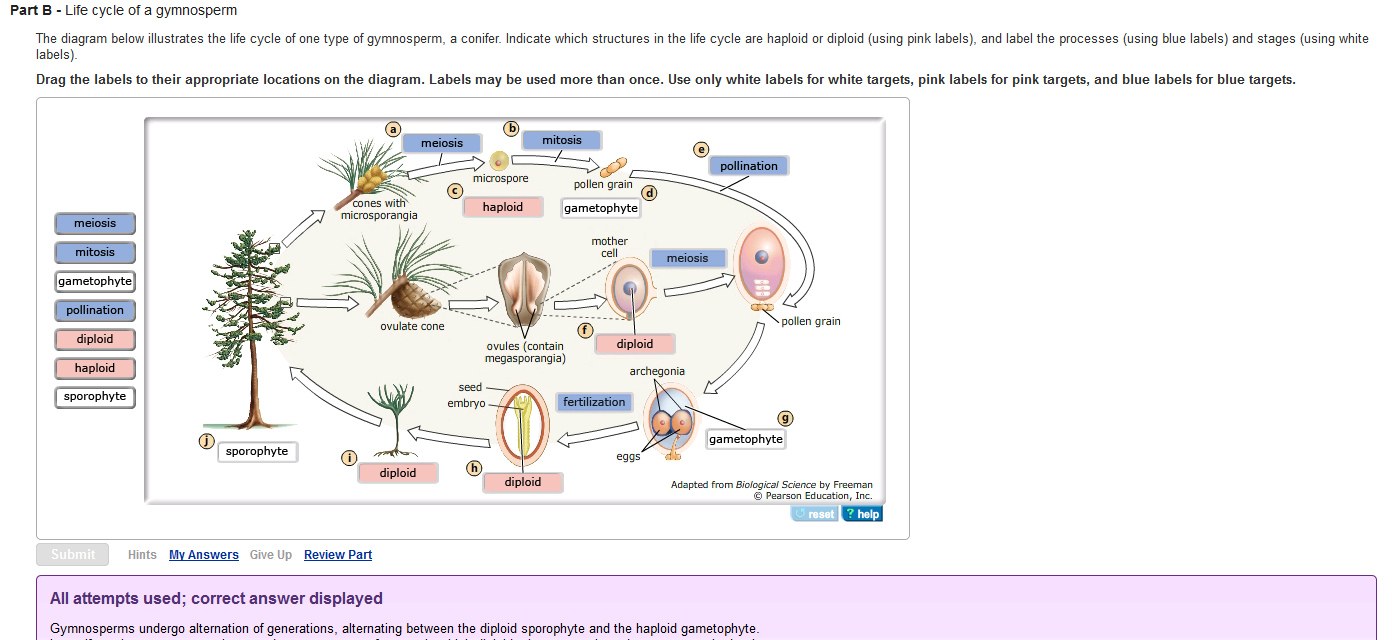
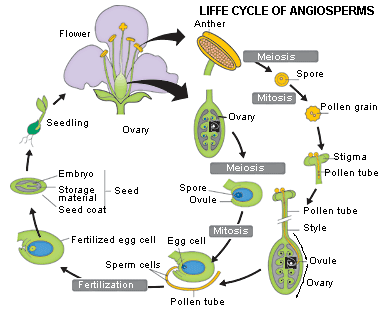
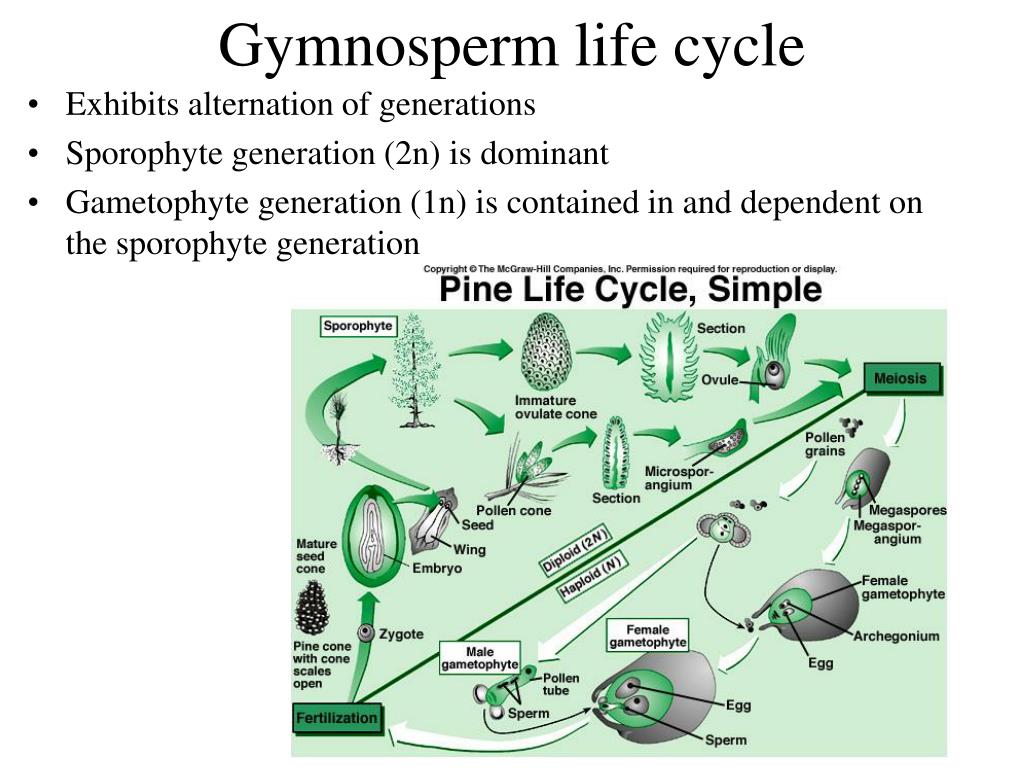
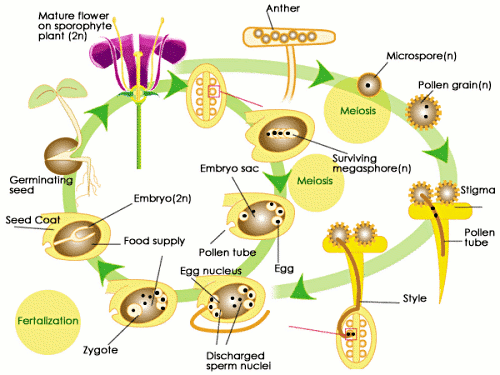
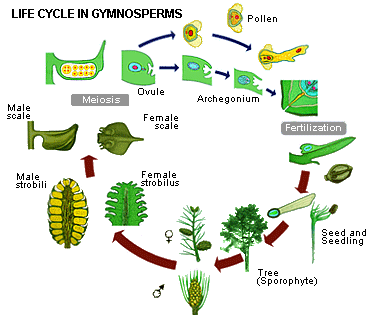
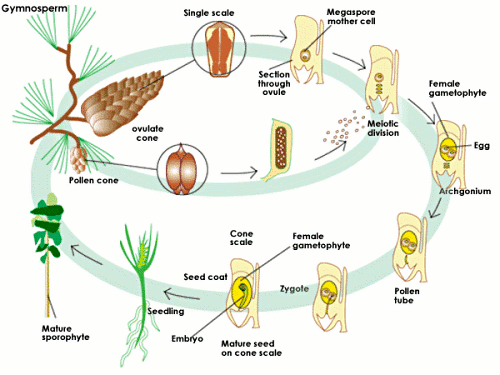
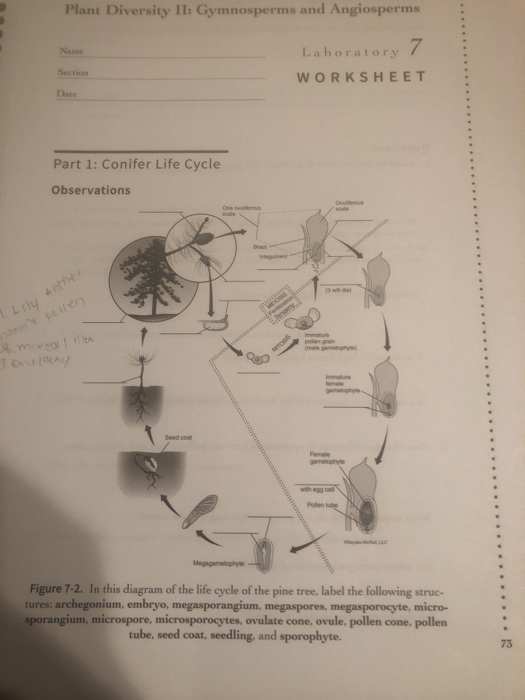
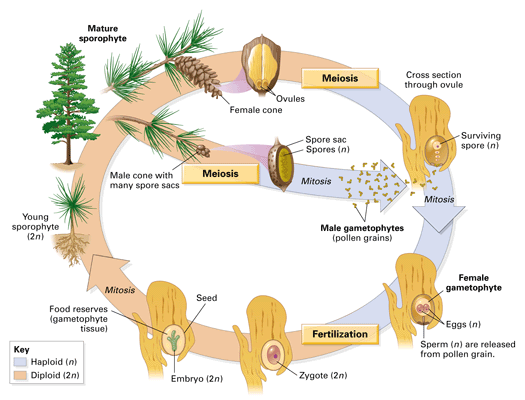
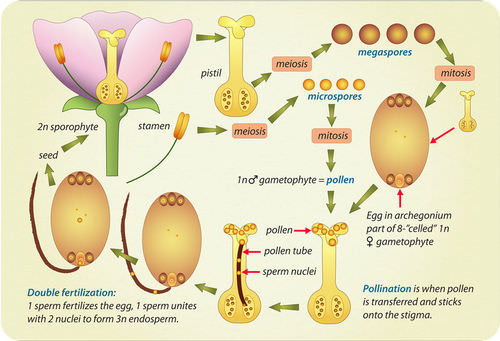
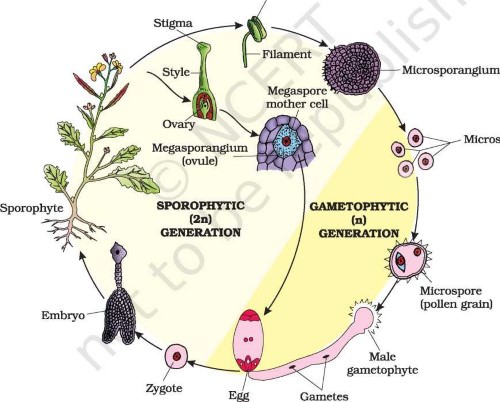
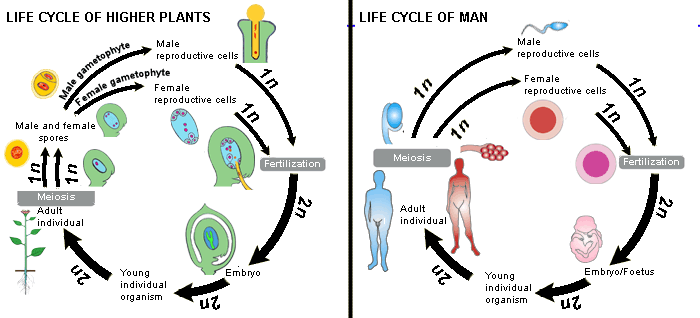
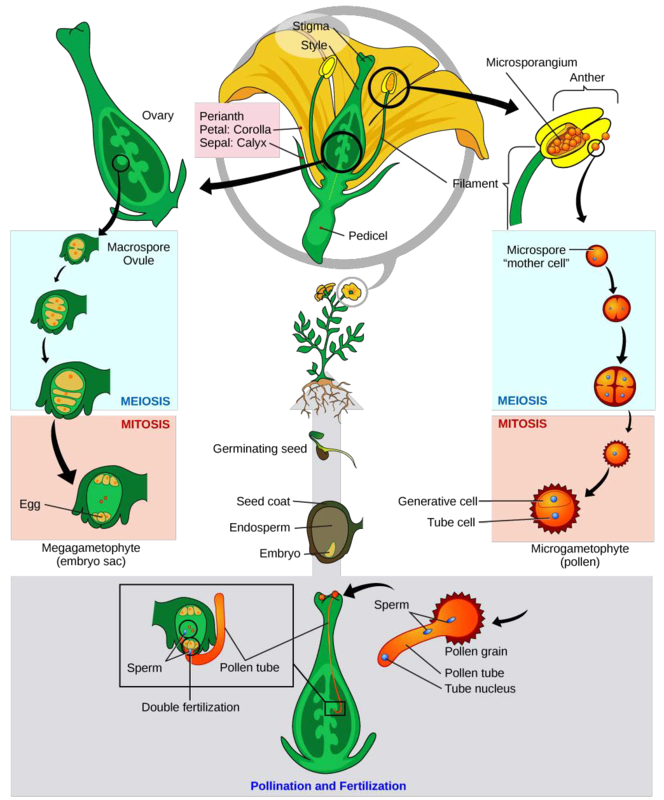
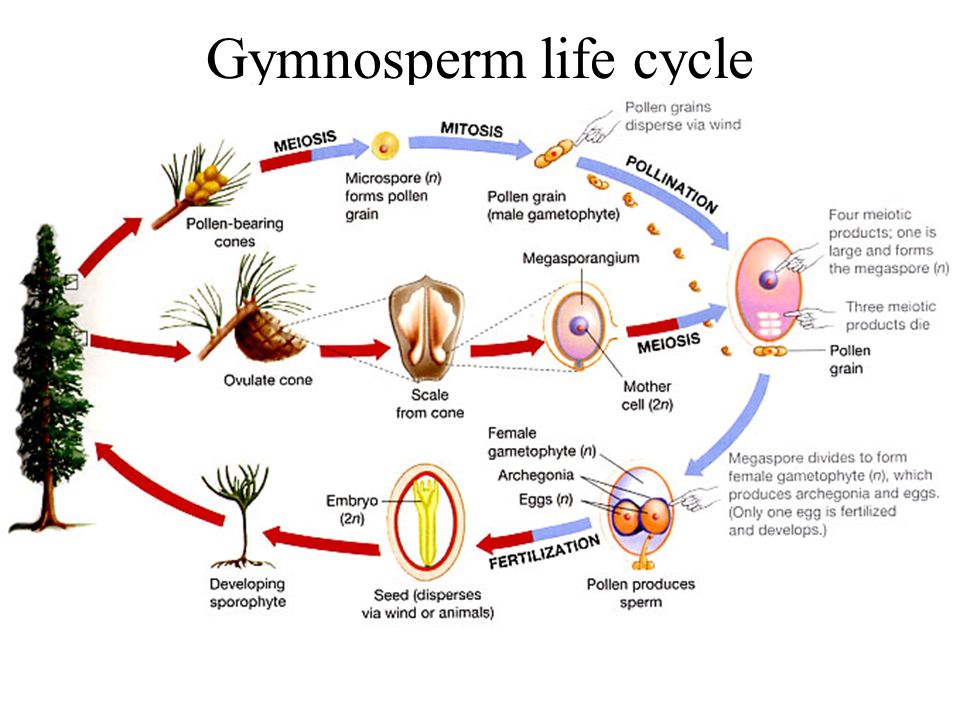
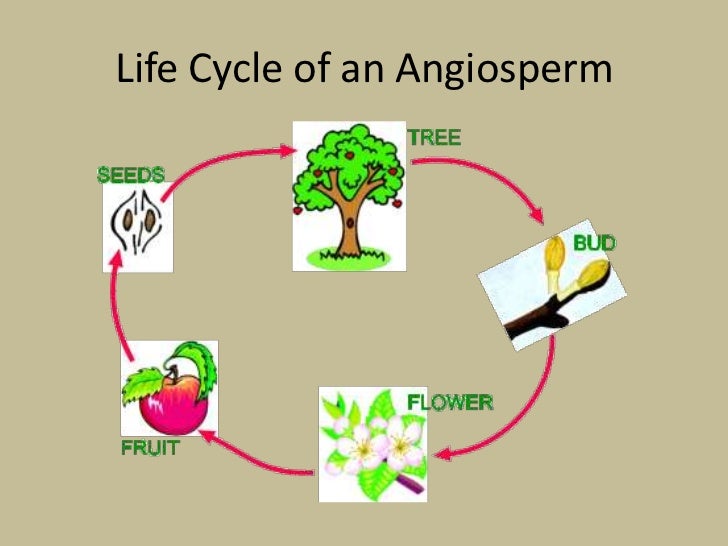
Life cycle of gymnosperms and angiosperms. They cycle between an asexual phase and a sexual phase. The sporophytes differentiate specialized reproductive structures called sporangia which are dedicated to the production of spores. In gymnosperms fertilization can occur up to a year after pollination whereas in angiosperms fertilization begins very soon after pollination. Angiosperm life cycle.
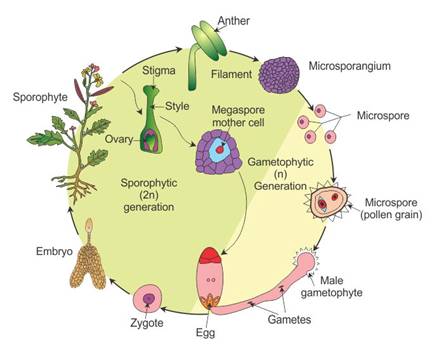
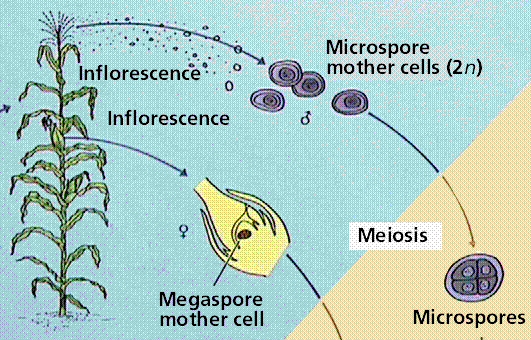
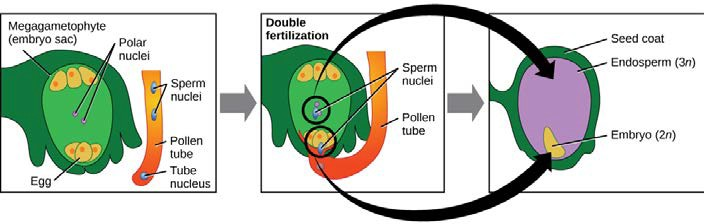
The shorter amount of time between pollination and fertilization allows angiosperms to produce seeds earlier after pollination than gymnosperms providing angiosperms a distinct evolutionary advantage. The sexual phase involves the production of gametes and is called the gametophyte generation. The microsporangium contains microspore mother cells which divide by meiosis to produce haploid. The main difference between angiosperms and gymnosperms is their diversity.
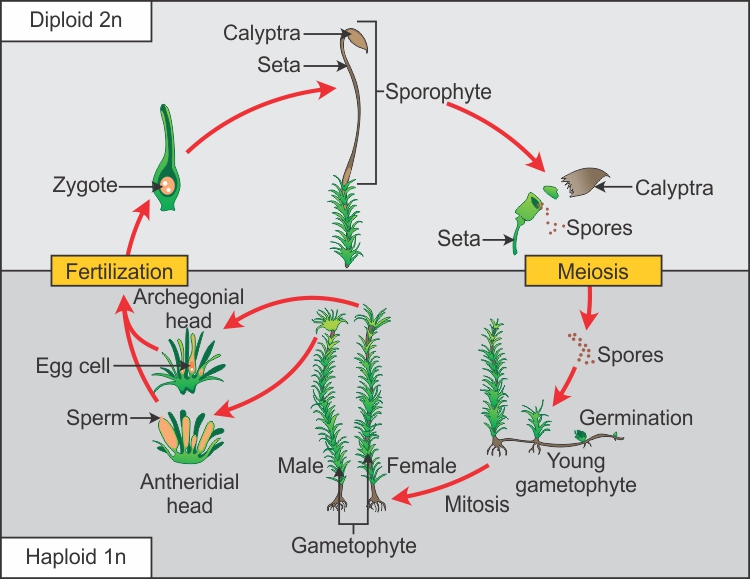
The asexual phase is called the sporophyte generation as it involves the production of spores. A fern plant in the diploid stage is known as the sporophyte. From the protonema grows the adult gametophyte which is the persistent and independent stage in the life cycle this stage usually grows as a thin rosette or ribbon like thallus between one and five centimeters in diameter and several layers of cells in thickness. Angiosperms grow and reproduce by a process called alternation of generations.
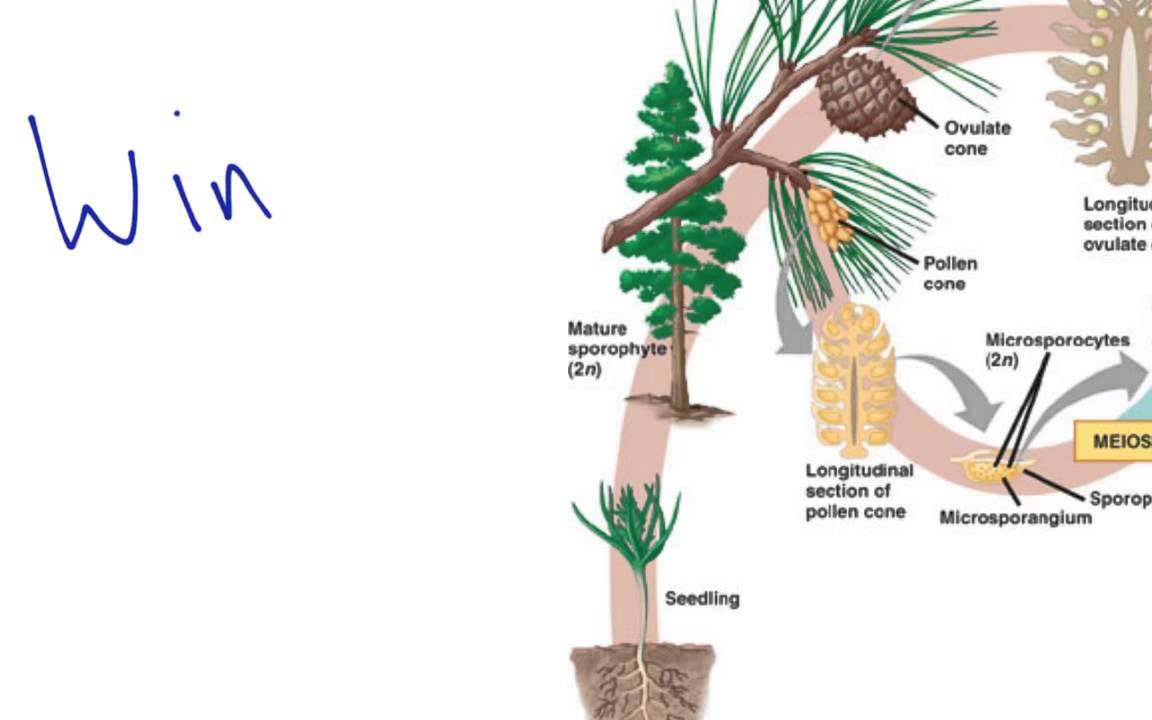
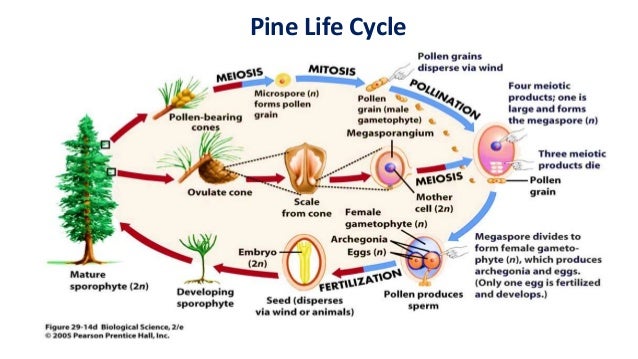
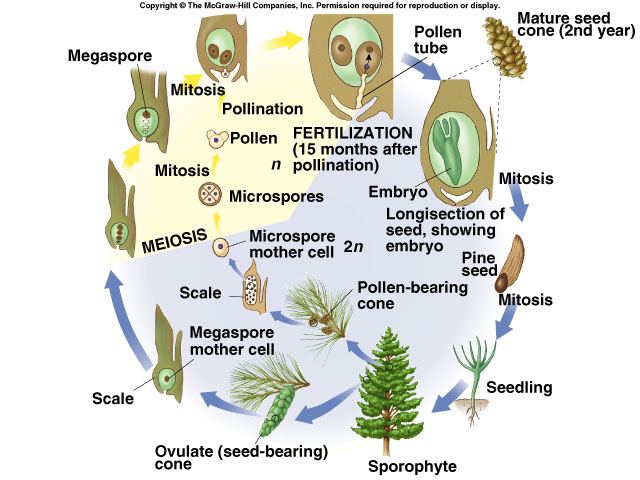
The gametophytes 1n microspores and megaspores are reduced in size. This phase may take more than one year between pollination and fertilization while the pollen tube grows towards the megasporocyte 2n which undergoes meiosis into megaspores. In the life cycle of a conifer the sporophyte 2n phase is the longest phase. All angiosperms have flowers at some stage in their life.
These sporangia produce haploid spore. As in all other vascular plants gymnosperms have a sporophyte dominant life cycle the sporophyte is the diploid multicellular stage which comprises the body of the plant i e a leafy tree. Ferns and other plants feature an interesting life cycle known as the alternation of generations. Gymnosperms and angiosperms have a life cycle that involves the alternation of generations and both have a reduced gametophyte stage.
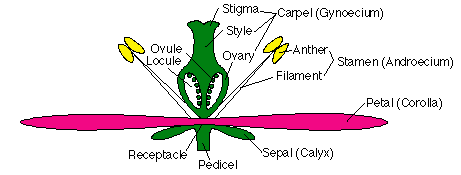
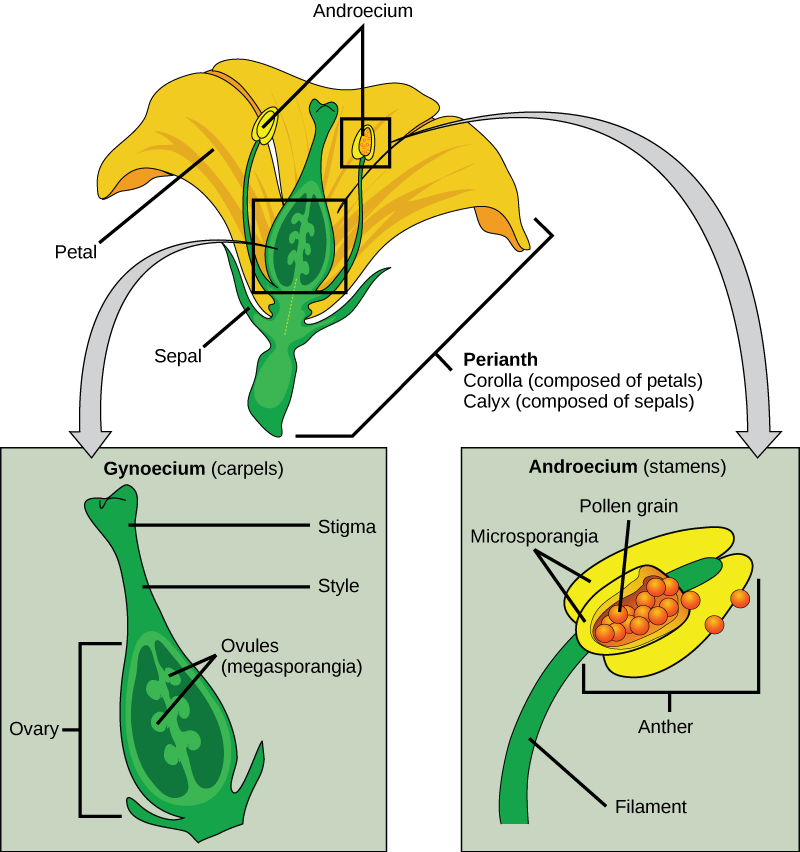
The flowers serve as the reproductive organs for the plant providing them a means of exchanging genetic information.

https www shutterstock com image vector gymnosperm vs angiosperm vector illustration labeled 1688997337