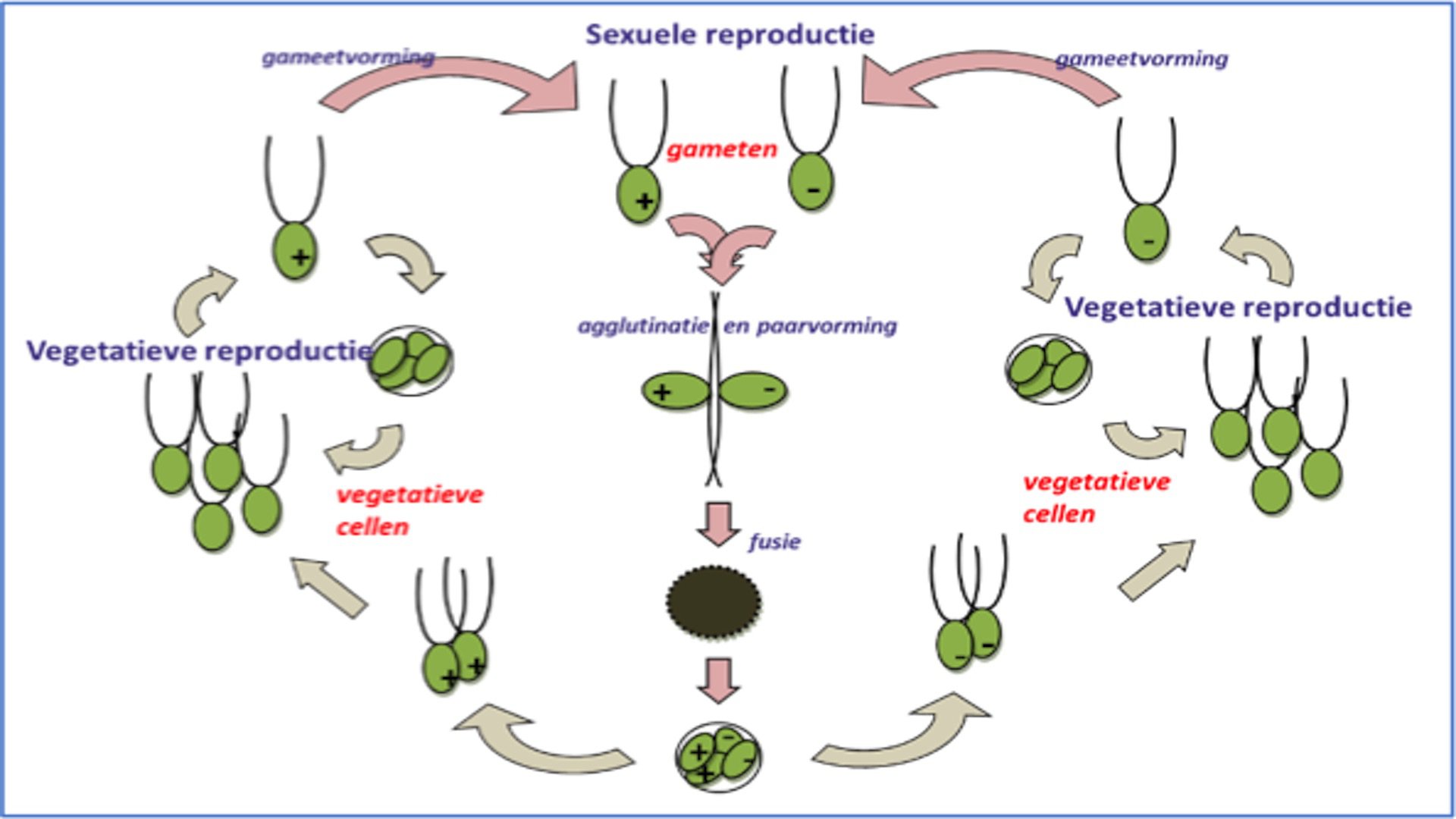
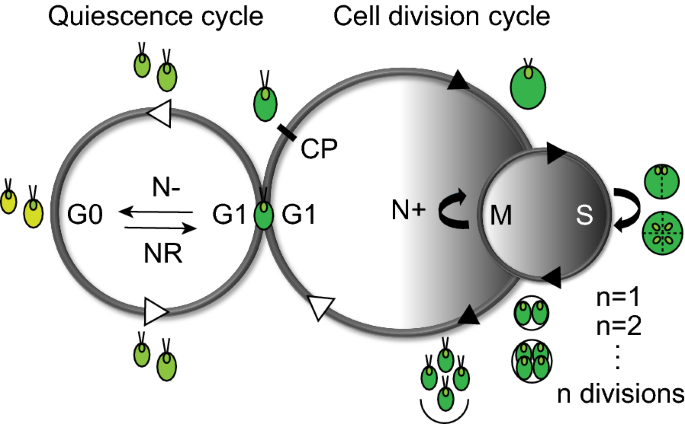
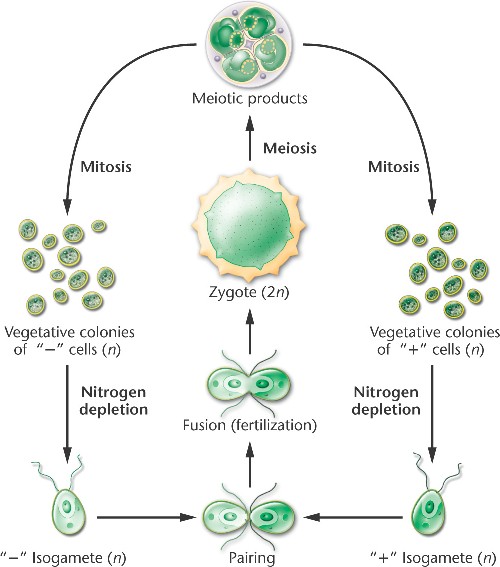
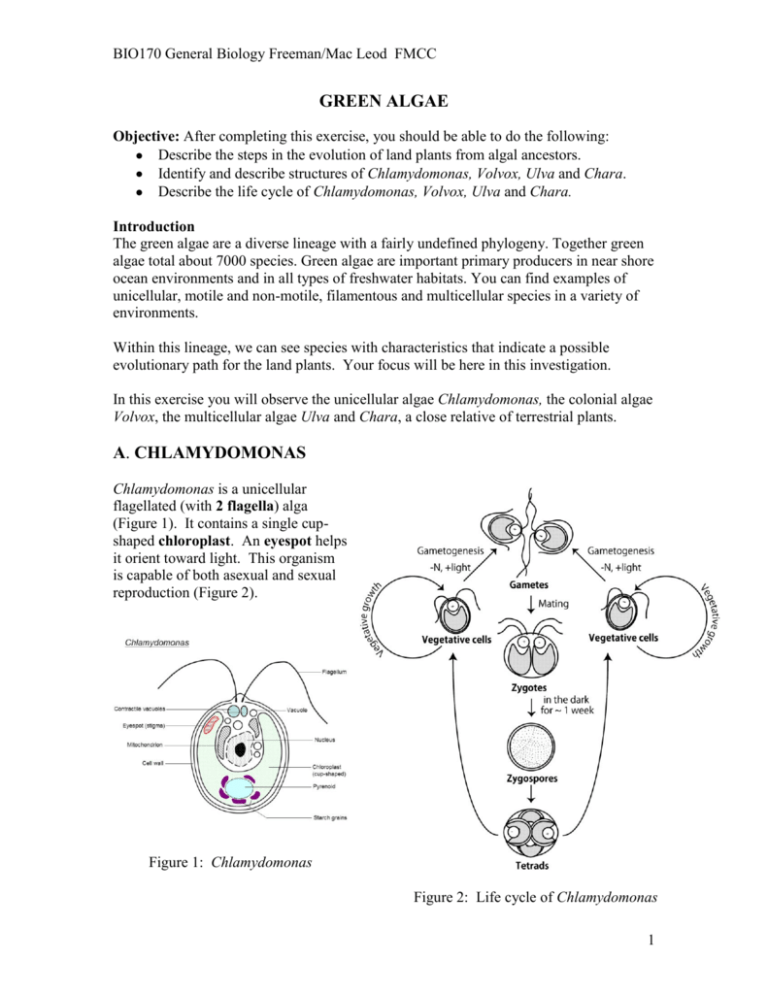
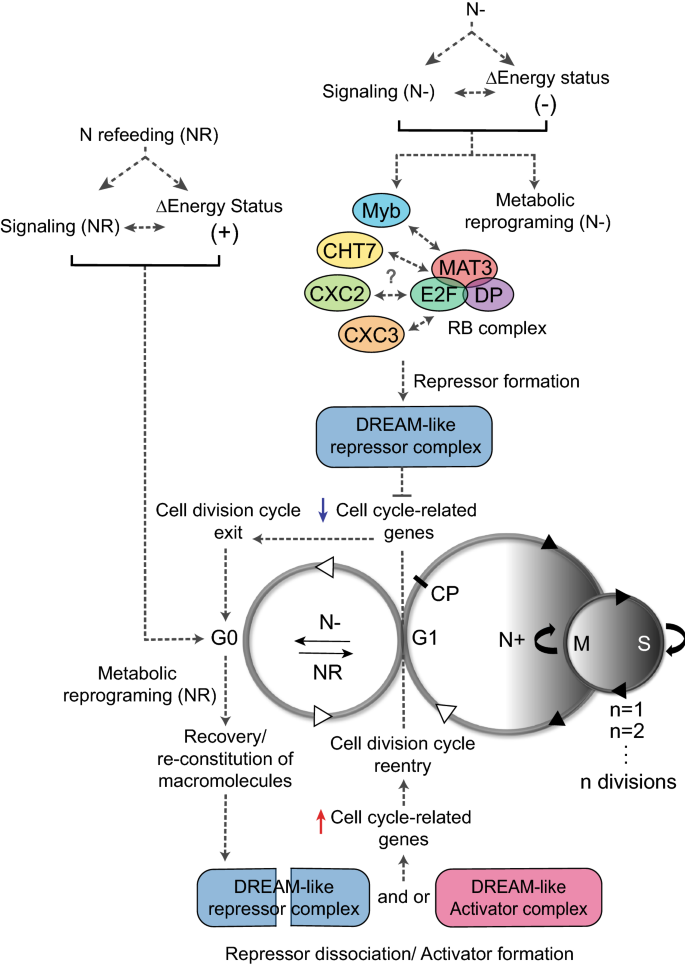
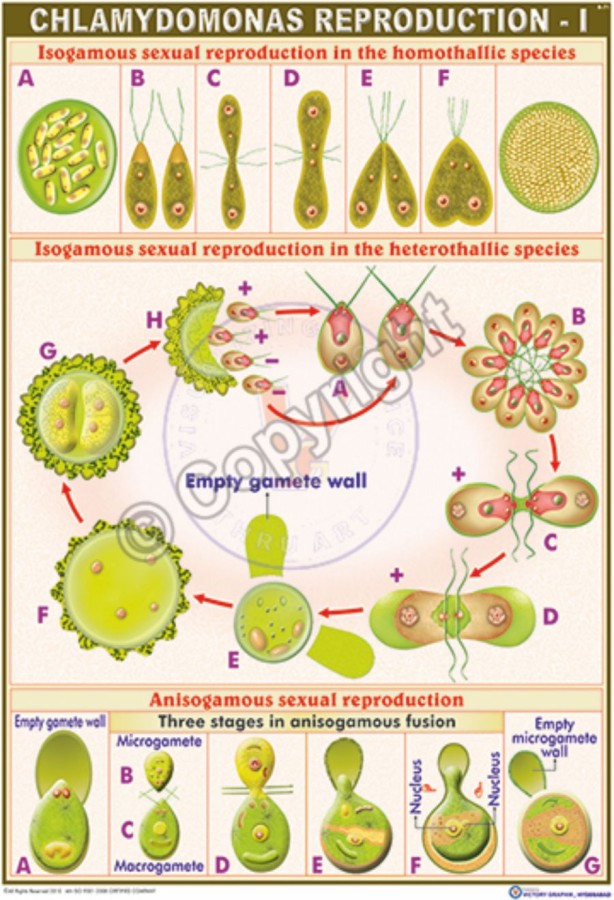
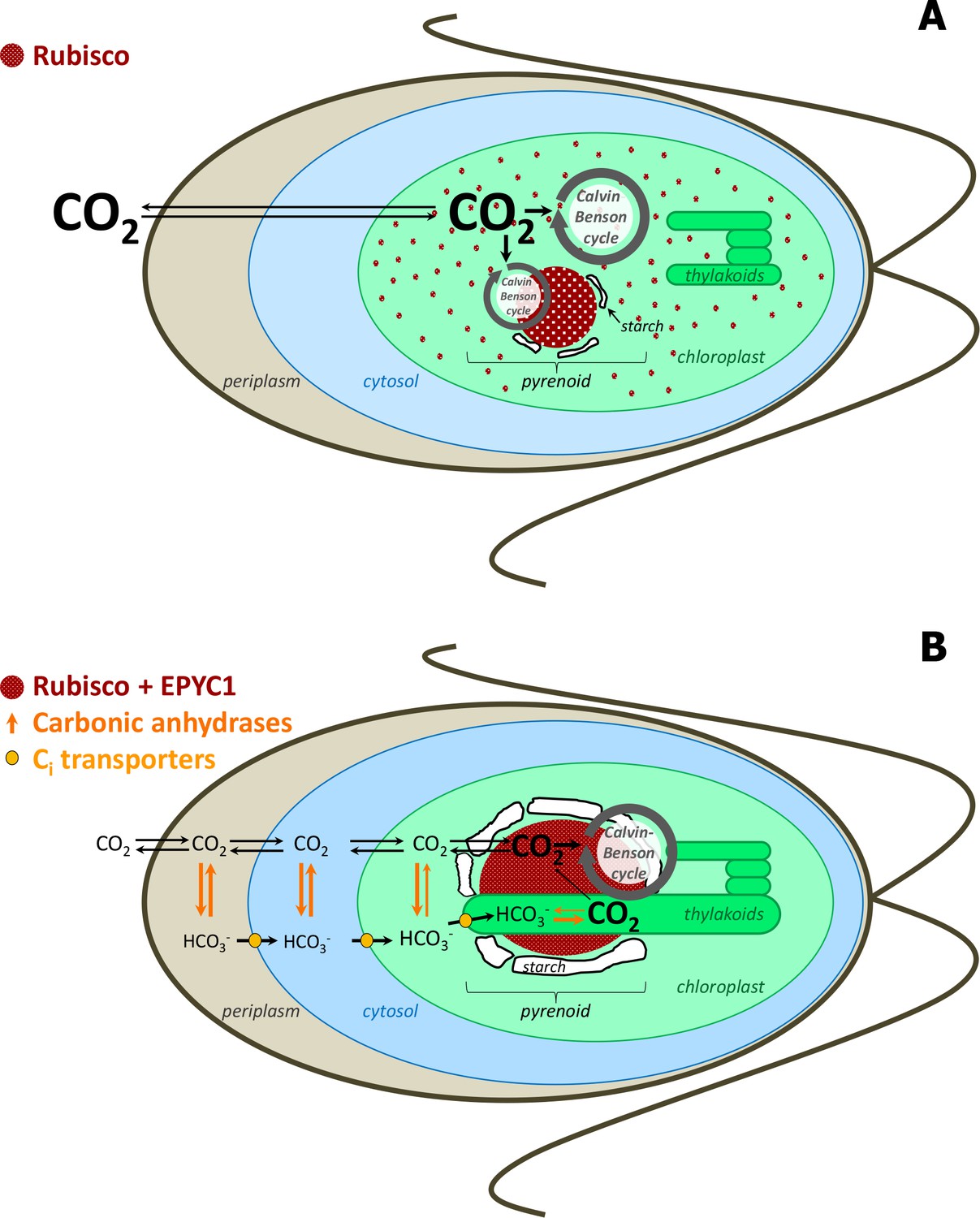
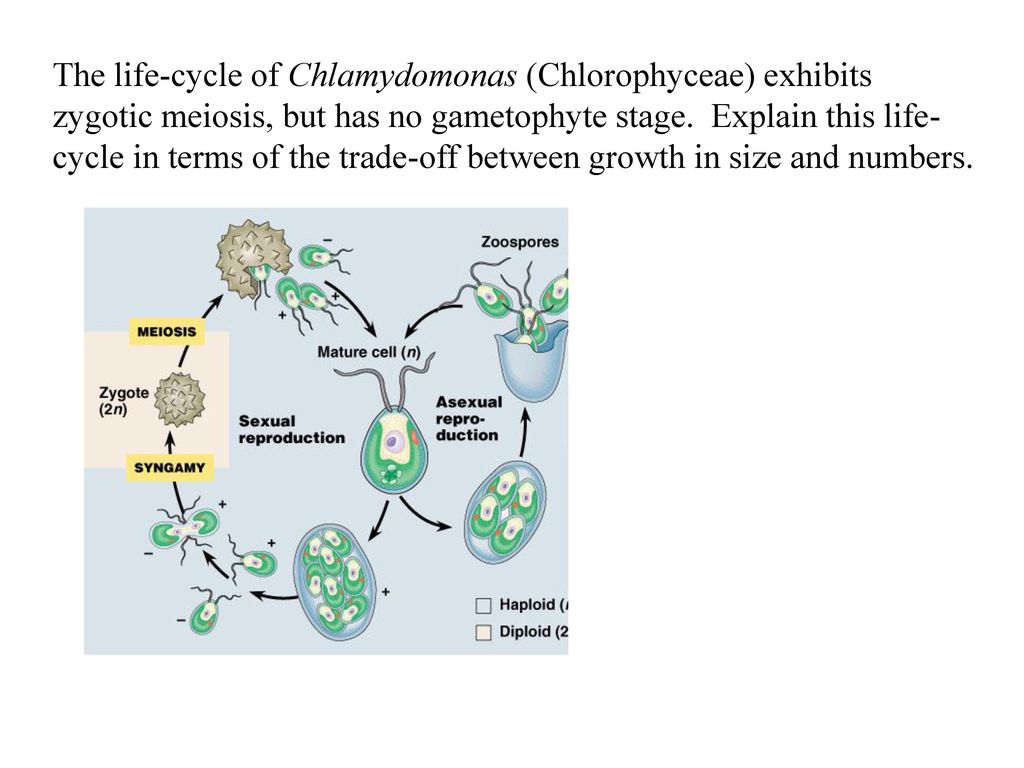
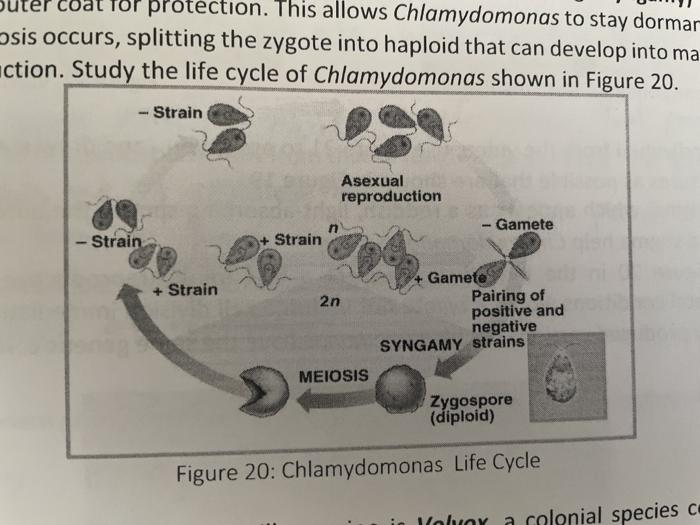
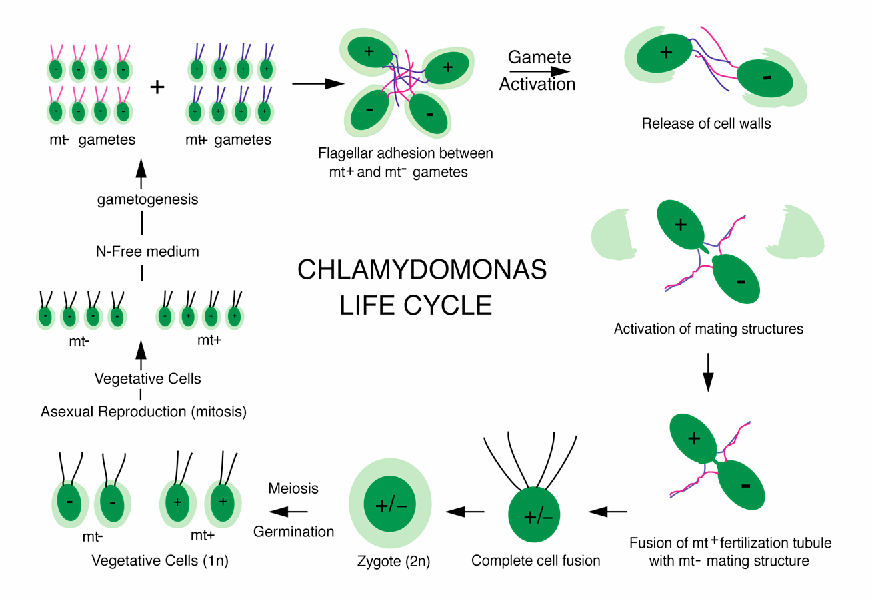
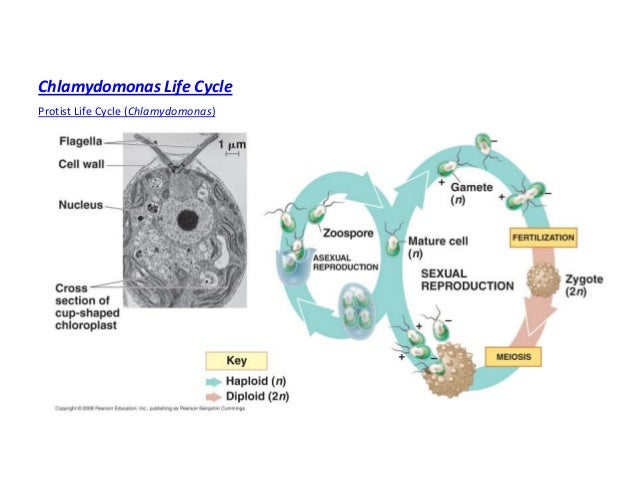
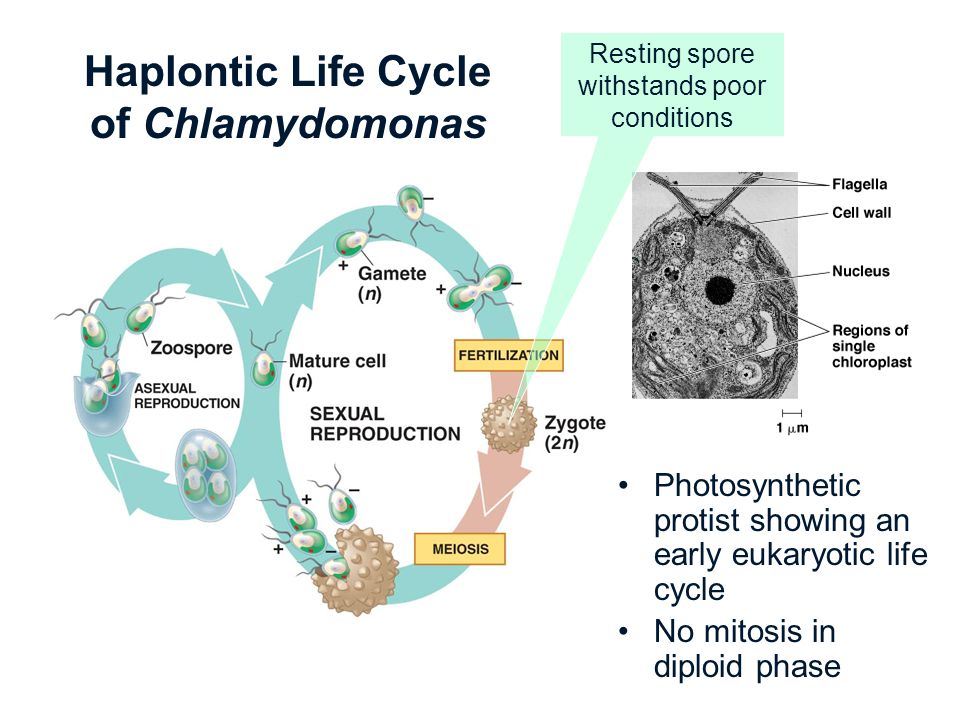
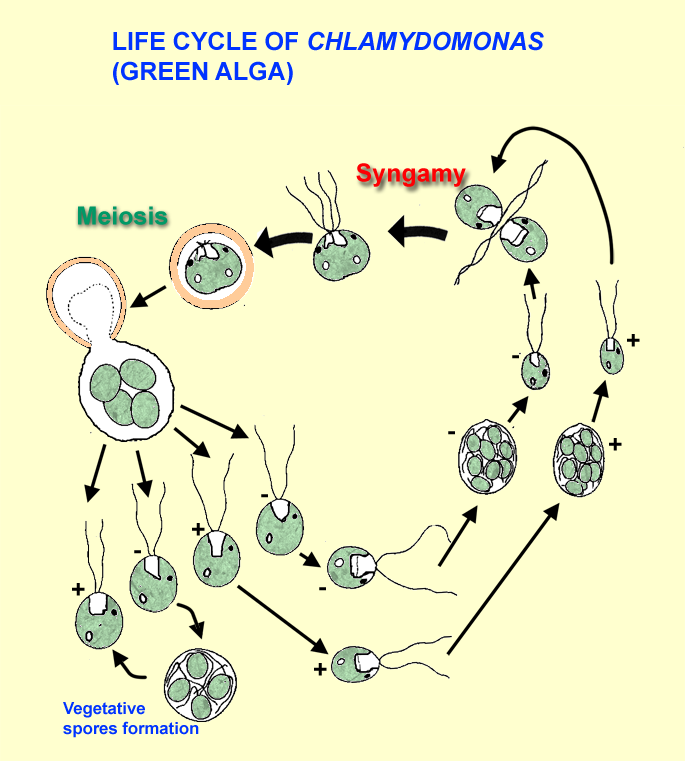
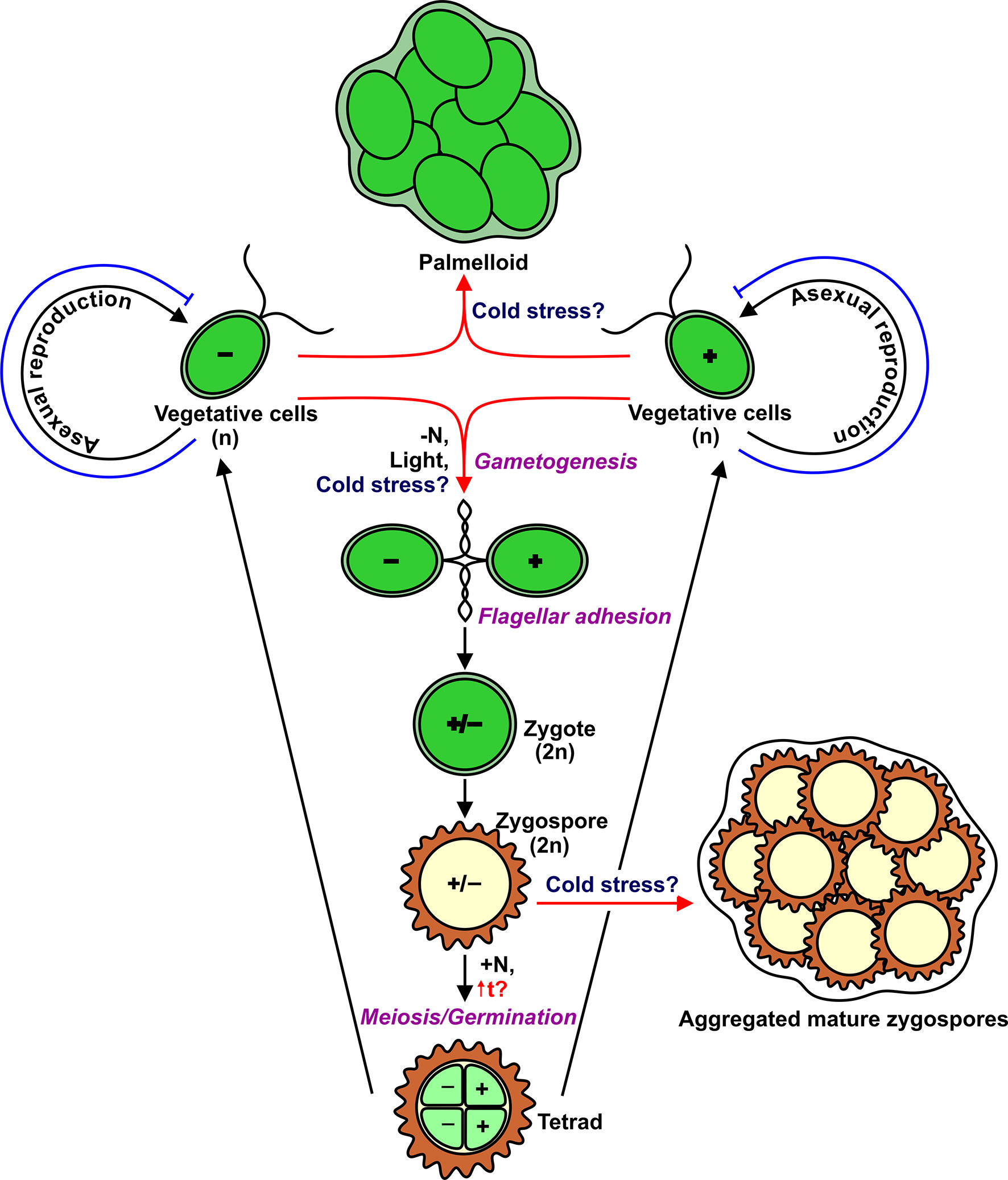
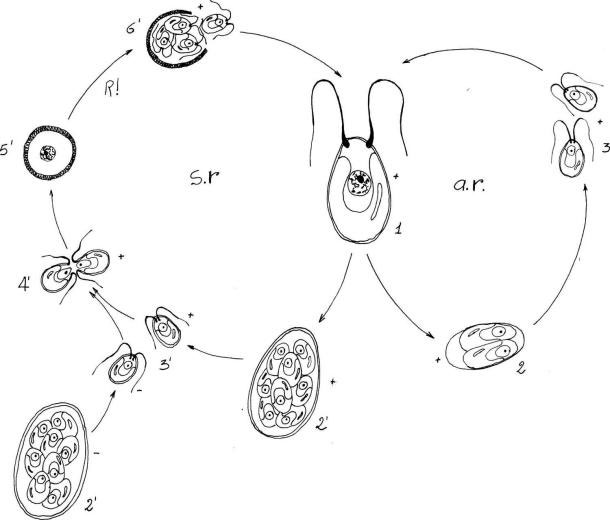
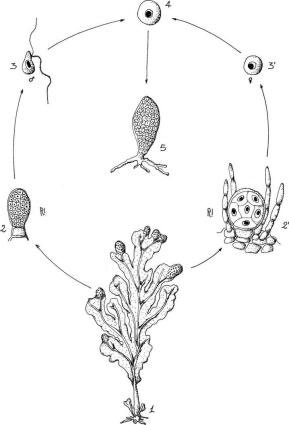
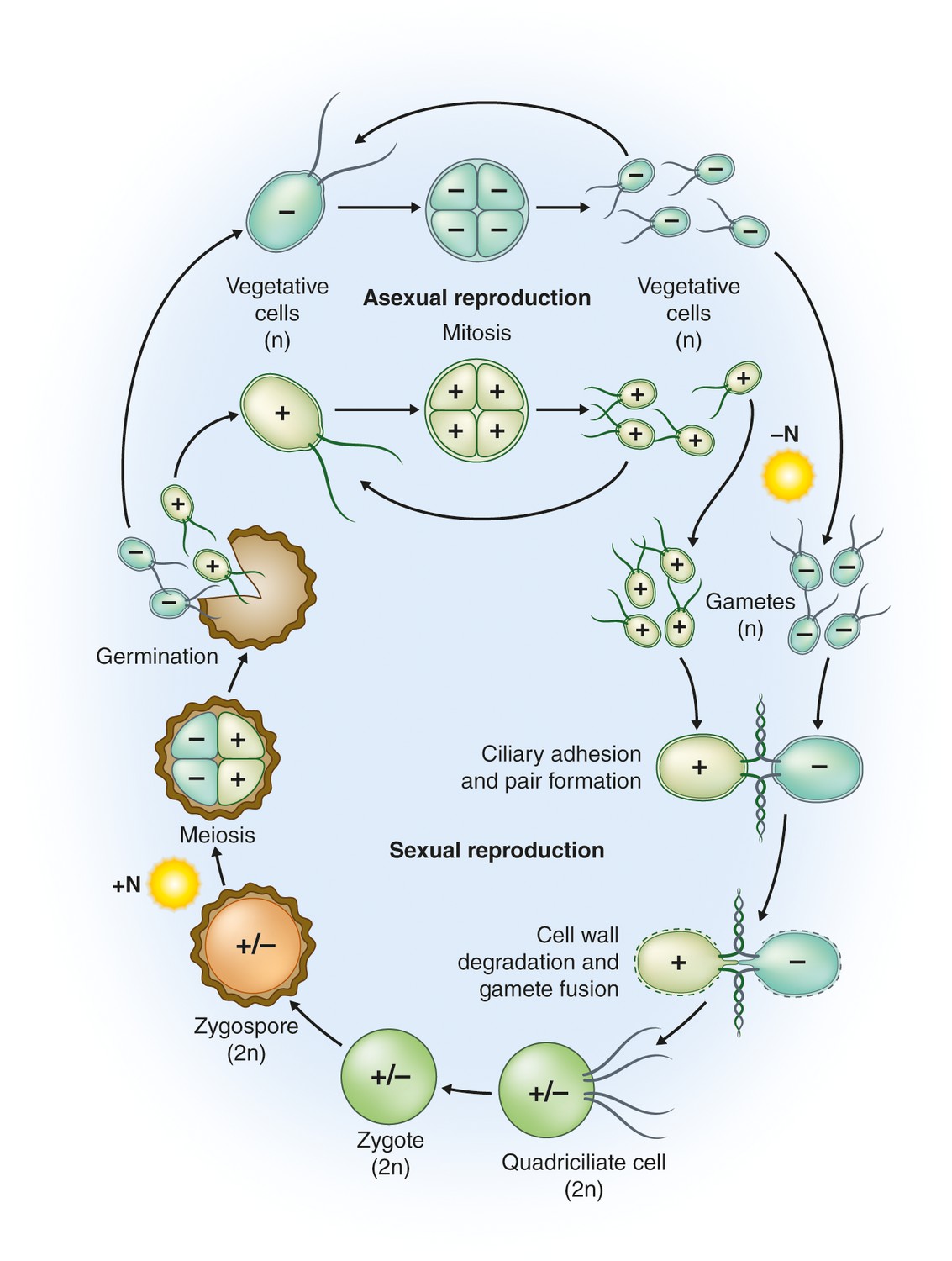
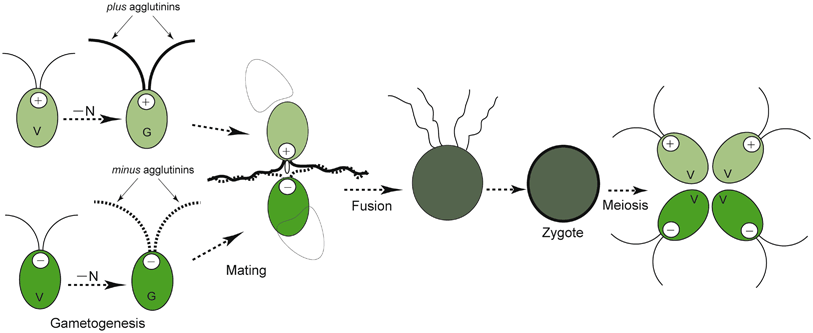
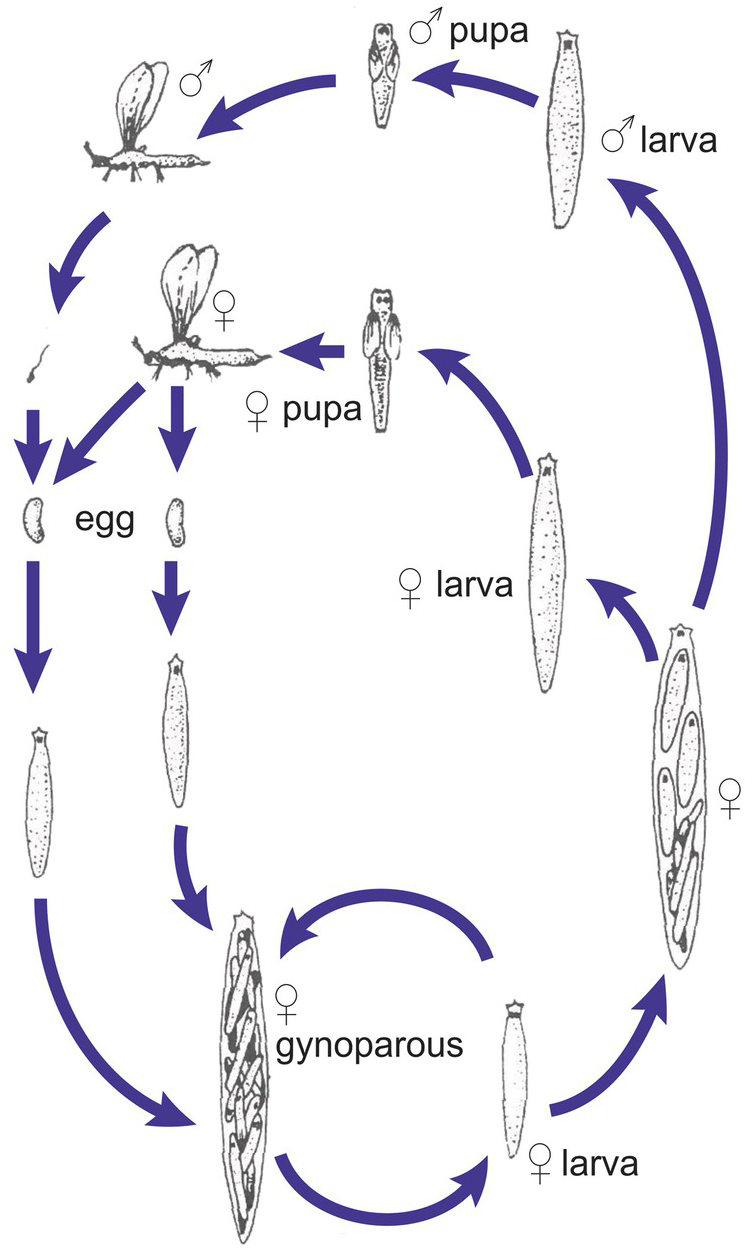
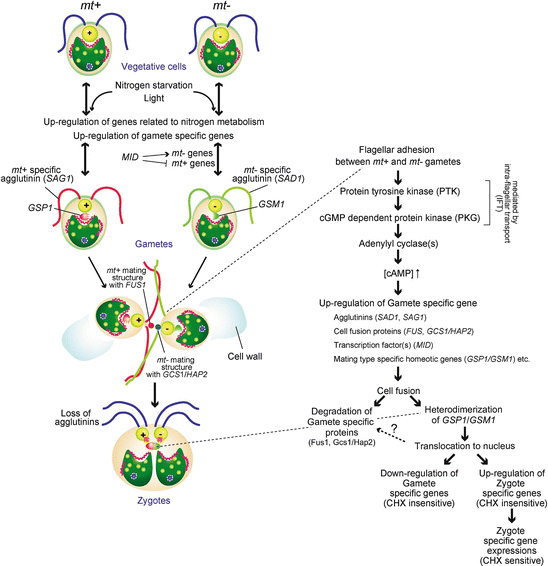
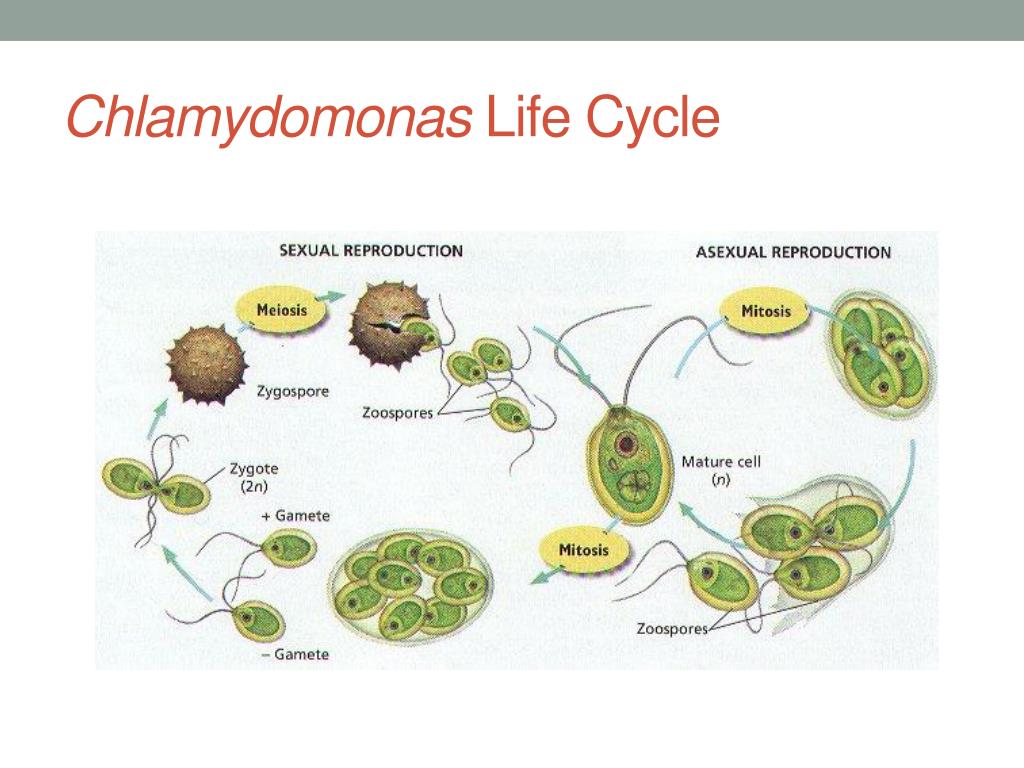
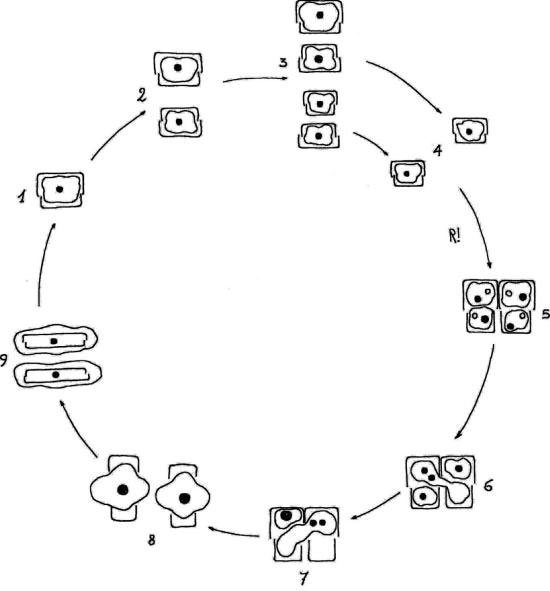
life cycle of chlamydomonas
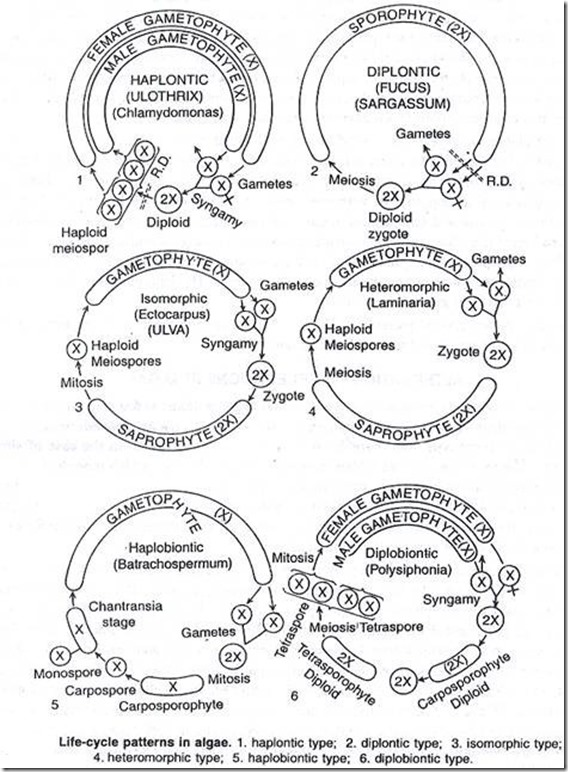
B diplontic life cycle. The life cycle of t. The life cycle characterized by gametic meiosis and diploid sporophyte this is dominant photosynthetic and independent generation of the plant.
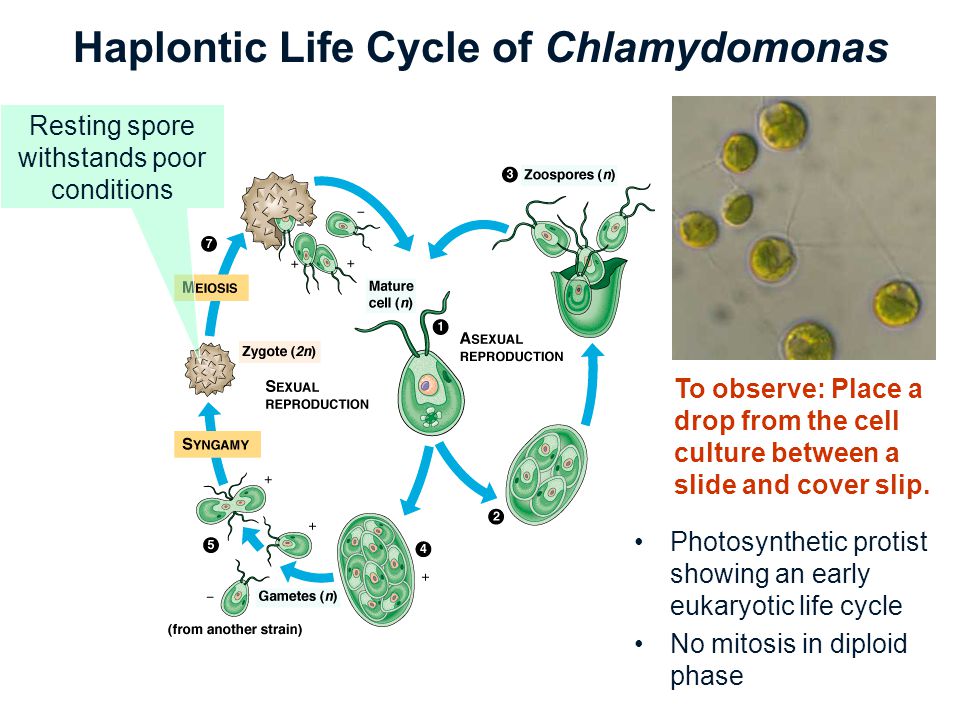
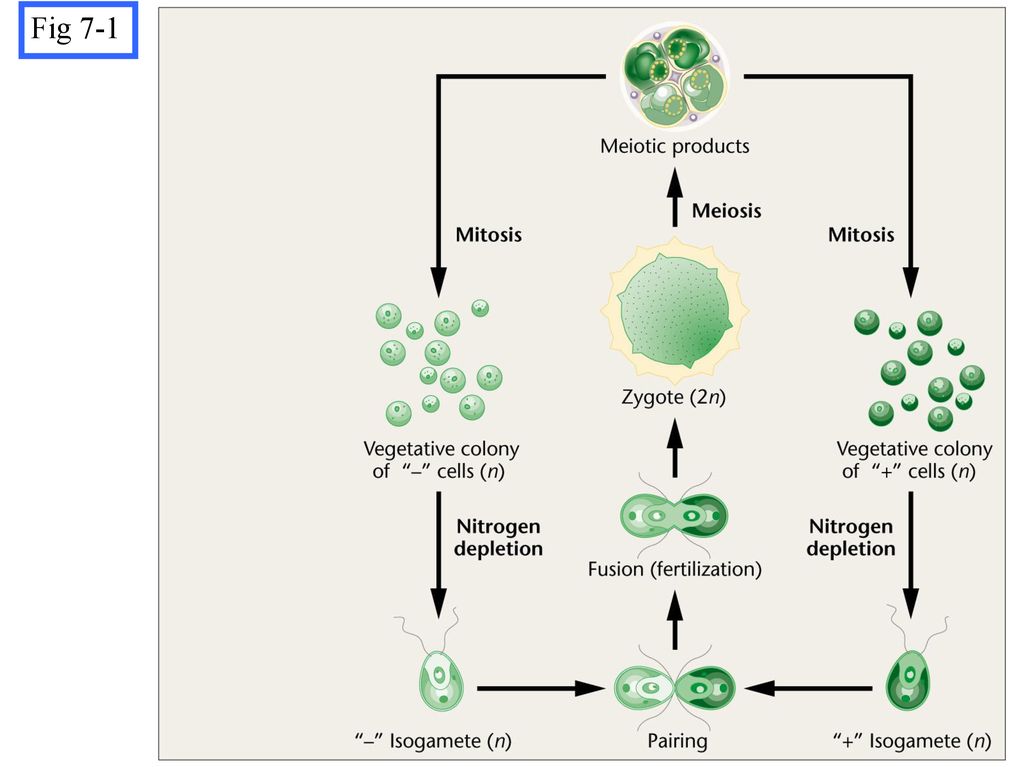
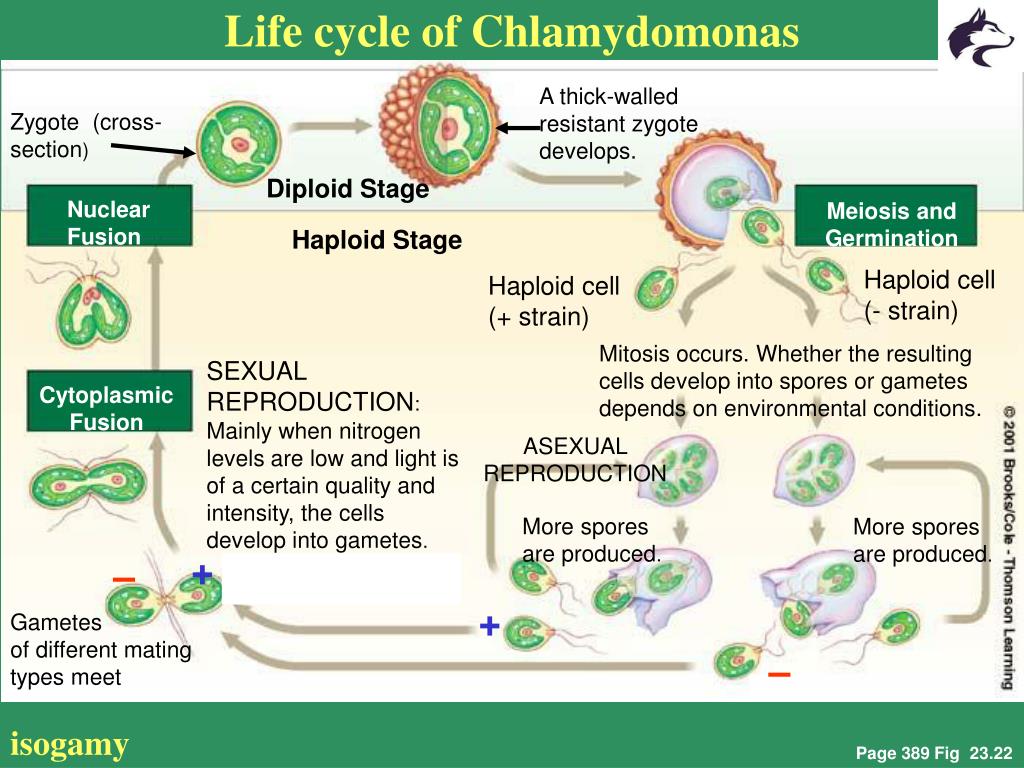
Chlamydomonas is a genus of green algae consisting of about 325 species all unicellular flagellates found in stagnant water and on damp soil in freshwater seawater and even in snow as snow algae.
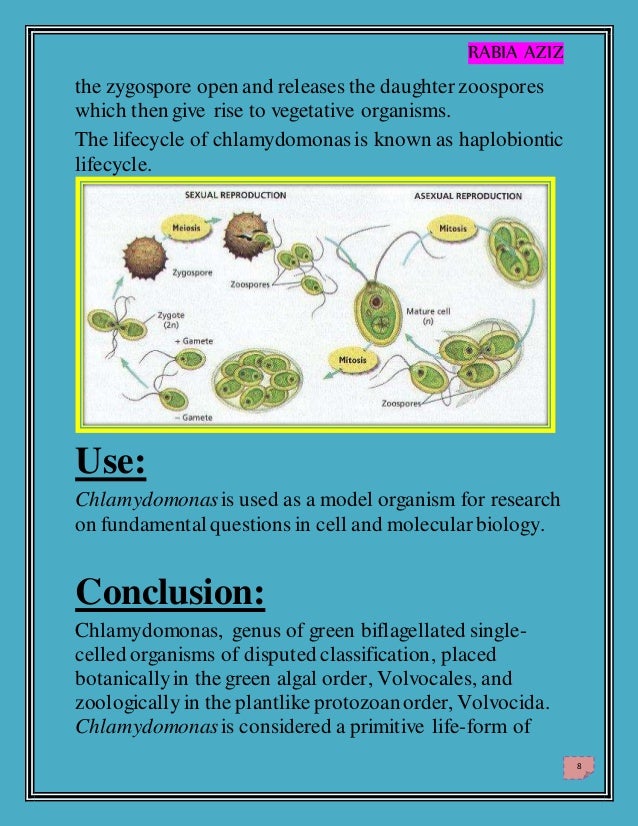
Life cycle of chlamydomonas. Life cycle of rhizopus. Volvox spirogyra chlamydomonas etc. The concept is closely related to those of the life history development and ontogeny but differs from them in stressing renewal transitions of form may involve growth asexual reproduction or. Chlamydomonas is used as a model organism for molecular biology especially studies of flagellar motility and chloroplast dynamics biogenesis and genetics.
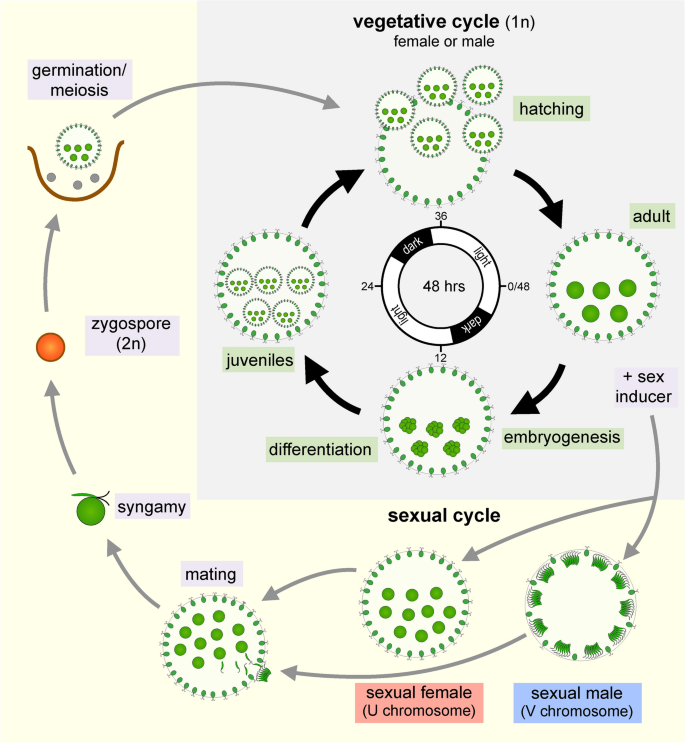
This type of cell division occurs by a sequence of morphogenetic events that results in the development of duplicate sets of cell structures one for each daughter cell. In nutrient rich media during vegetative growth cells reproduce asexually by binary fission. Life cycle when conditions are unfavourable due to prolonged dryness or exposure to low salinity waters dunaliella cells undergo sexual reproduction. The gametophyte generation is represented by the haploid gametes.
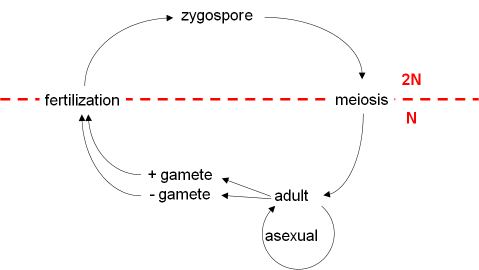
Then this chlamydospore gets detached from vegetative hyphae and they remain in resting phase and when this chlamydomonas gets enough moisture they undergo the formation of germ tube which leads to formation of new thallus. Chlamydomonas species can become so abundant as to colour fresh water green and one species c. Nivalis contains a red pigment known as hematochrome which sometimes imparts a red colour to melting snow. In biology a biological life cycle or just life cycle or lifecycle when the biological context is clear is a series of changes in form that an organism undergoes returning to the starting state.
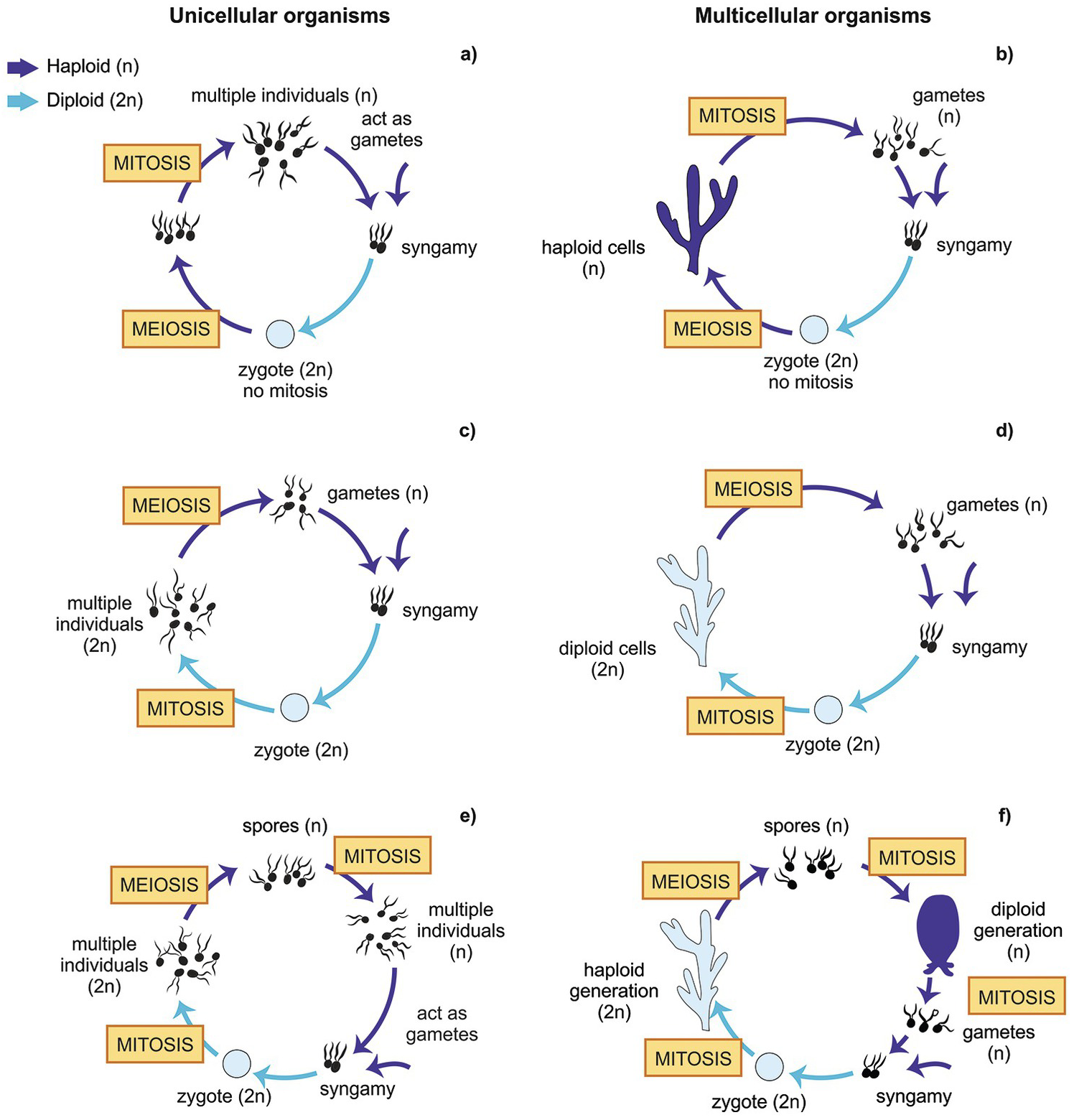
In this life cycle plants are haploid. Chlamydomonas genus of biflagellated single celled green algae family chlamydomonadaceae found in soil ponds and ditches. Marine life or sea life or ocean life is the plants animals and other organisms that live in the salt water of the sea or ocean or the brackish water of coastal estuaries at a fundamental level marine life affects the nature of the planet. The zygote divides meiotically to form haploid cells which undergo mitosis to form multicellular haploid organisms.
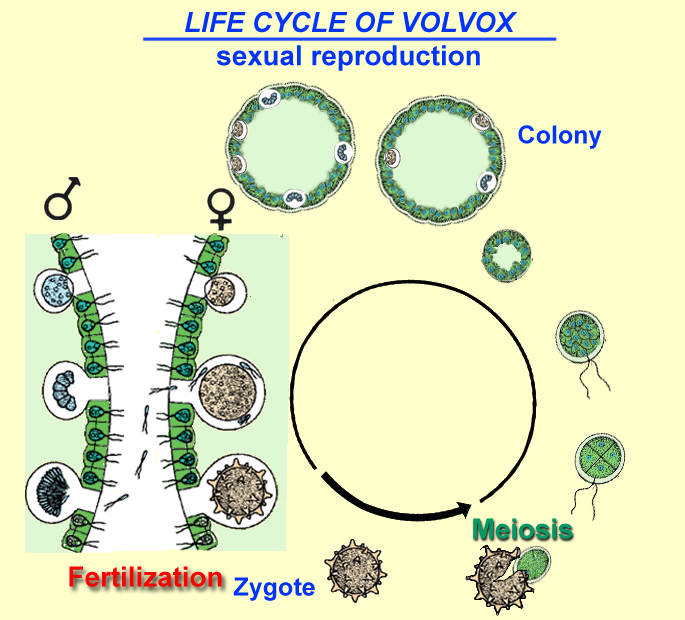
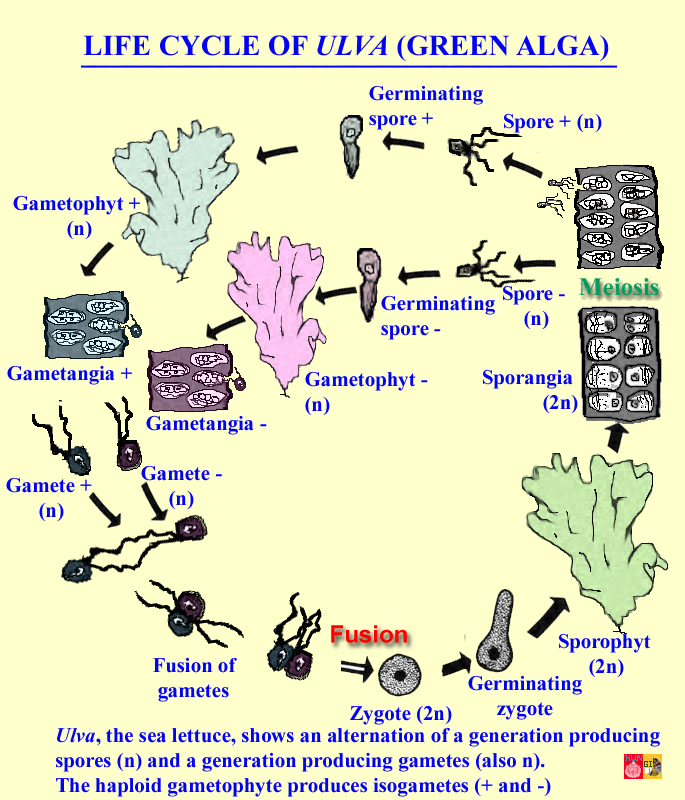
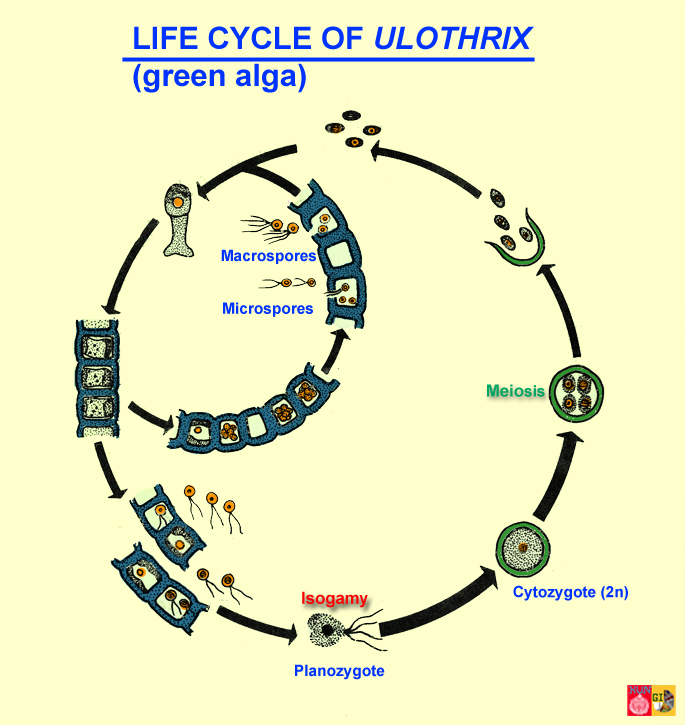
Sequential changes of the different pages through which an organism completes the life process starting from zygote to the zygote of the next generation is called the life cycle. Marine organisms mostly microorganisms produce oxygen and sequester carbon shorelines are in part shaped and protected by marine life and some. Life cycle of algae. Two haploid vegetative motile cells will touch flagella and then fuse their equal sized gametes with one another in a very similar way to chlamydomonas by the formation of a cytoplasmic bridge.
Diplontic life cycle the diploid sporophyte is the dominant stage. There are four types of life cycle in algae such as. It shows gametic meiosis. Diploid stage is not free living.